Continental climate
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2007) |

Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm to hot summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in central and eastern parts of the three northern-tier continents (North America, Europe, and Asia), typically in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 or 60 degrees north), often within large landmasses, where prevailing winds blow overland bringing some precipitation, and temperatures are not moderated by oceans. Continental climates occur mostly in the Northern Hemisphere due to the large landmasses found there. Most of northeastern China, eastern and southeastern Europe, much of Russia south of the Arctic Circle, central and southeastern Canada, and the central and northeastern United States have this type of climate.[1] Continentality is a measure of the degree to which a region experiences this type of climate.[1]
In continental climates, precipitation tends to be moderate in amount, concentrated mostly in the warmer months. Only a few areas—in the mountains of the Pacific Northwest of North America and in Iran, northern Iraq, adjacent Turkey, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Central Asia—show a winter maximum in precipitation. A portion of the annual precipitation falls as snowfall, and snow often remains on the ground for more than a month. Summers in continental climates can feature thunderstorms and frequent hot temperatures; however, summer weather is somewhat more stable than winter weather. Continental climates are considered as temperate climate varieties due to their location in the temperate zones,[2][3] but are classified separately from other temperate climates in the Köppen climate classification system where they are identified by their first letter, a capital D. In the Trewartha climate classification, they are identified as Dc.
Köppen climate classification
[edit]Continental climate has at least one month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) and at least one month averaging above 10 °C (50 °F).[4][5]
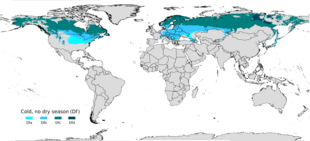
- Dfa = Hot-summer humid continental climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)), at least one month's average temperature above 22 °C (71.6 °F), and at least four months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). No significant precipitation difference between seasons (neither the abovementioned set of conditions fulfilled).
- Dfb = Warm-summer humid continental climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)), all months with average temperatures below 22 °C (71.6 °F), and at least four months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). No significant precipitation difference between seasons (neither the abovementioned set of conditions fulfilled).
- Dfc = Subarctic climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)) and one–three months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). No significant precipitation difference between seasons (neither the abovementioned set of conditions fulfilled).
- Dfd = Extremely cold subarctic climate; coldest month averaging below −38 °C (−36.4 °F) and one–three months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). No significant precipitation difference between seasons (neither the abovementioned set of conditions fulfilled).

- Dwa = Monsoon-influenced hot-summer humid continental climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)), at least one month's average temperature above 22 °C (71.6 °F), and at least four months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least ten times as much rain in the wettest month of summer as in the driest month of winter.
- Dwb = Monsoon-influenced warm-summer humid continental climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)), all months with average temperatures below 22 °C (71.6 °F), and at least four months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least ten times as much rain in the wettest month of summer as in the driest month of winter.
- Dwc = Monsoon-influenced subarctic climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)) and one–three months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least ten times as much rain in the wettest month of summer as in the driest month of winter.
- Dwd = Monsoon-influenced extremely cold subarctic climate; coldest month averaging below −38 °C (−36.4 °F) and one–three months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least ten times as much rain in the wettest month of summer as in the driest month of winter.
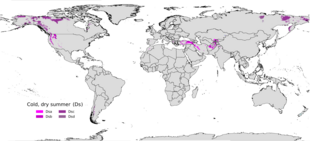
- Dsa = Mediterranean-influenced hot-summer humid continental climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)), average temperature of the warmest month above 22 °C (71.6 °F) and at least four months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least three times as much precipitation in the wettest month of winter as in the driest month of summer, and the driest month of summer receives less than 30 mm (1.2 in).
- Dsb = Mediterranean-influenced warm-summer humid continental climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)), average temperature of the warmest month below 22 °C (71.6 °F) and at least four months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least three times as much precipitation in the wettest month of winter as in the driest month of summer, and the driest month of summer receives less than 30 mm (1.2 in).
- Dsc = Mediterranean-influenced subarctic climate; coldest month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)) and one–three months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least three times as much precipitation in the wettest month of winter as in the driest month of summer, and the driest month of summer receives less than 30 mm (1.2 in).
- Dsd = Mediterranean-influenced extremely cold subarctic climate; coldest month averaging below −38 °C (−36.4 °F) and one–three months averaging above 10 °C (50 °F). At least three times as much precipitation in the wettest month of winter as in the driest month of summer, and the driest month of summer receives less than 30 mm (1.2 in).
Seasons
[edit]Annual precipitation in this zone is usually between 600 millimetres (24 in) and 1,200 millimetres (47 in), The timing of intermediate spring-like or autumn-like temperatures in this zone vary depending on latitude and/or elevation. For example, spring may arrive as soon as March (in Northern hemisphere, September in Southern hemisphere) in the southern (in Northern hemisphere, northern in Southern hemisphere), parts of this zone or as late as May (November) in the north (south). Summers are warm or hot while winters are below freezing and sustain lots of frost.
Climatology
[edit]Continental climates exist where cold air masses infiltrate during the winter from shorter days and warm air masses form in summer under conditions of high sun and longer days. Places with continental climates are as a rule either far from any moderating effect of oceans or are so situated that prevailing winds tend to head offshore.[6] Such regions get quite warm in the summer, achieving temperatures characteristic of tropical climates but are colder than any other climates of similar latitude in the winter.
Neighboring climates
[edit]In the Köppen climate system, these climates grade off toward temperate climates equator-ward where winters are less severe and semi-arid climates or arid climates where precipitation becomes inadequate for tall-grass prairies and shrublands. In Europe these climates may grade off into oceanic climates (Cfb) or subpolar oceanic climates (Cfc) in which the influence of cool oceanic air masses is more marked toward the west. In western and eastern Asia, and the central United States these climates grade off toward humid subtropical climates (Cfa/Cwa), subtropical highland climates (Cwb), or Mediterranean climates (Csa/Csb) to the south.
List of locations with a continental climate
[edit]^1 The climate is continental if the 0°C coldest-month isotherm is used, but it is temperate if the -3°C isotherm is used.

- Afghanistan: Chaghcharan (Dsb), Fayzabad1 (Dsa bordering Csa), Ghazni (Dsa bordering BSk), Puli Alam (Dsa)
- Armenia: Gyumri, Jermuk (Dsb bordering Dfb), Kapan, Sisian, Vanadzor, Yerevan (bordering BSk)
- Azerbaijan: Qabala1 (bordering Cfa), Shamakhi1 (bordering Cfa)
- China: Anshan, Beijing1, Biru County, Changchun, Dalian, Daqing, Hailin, Harbin, Hulunbuir, Heihe, Jiamusi, Jilin, Jinan1 (bordering Cwa), Mudanjiang, Qiqihar, Shenyang, Shigatse1, Suihua, Tangshan, Ulanhot, Ürümqi (bordering BSk), Xi'an1 (bordering Cwa), Yanji, Yantai1, Yichun
- Georgia: Akhaltsikhe1
- India: Badrinath1 (bordering Cfb), Dras (Dsb bordering Dfb)
- Iran: Abali (Dsb), Arak1 (Dsa bordering BSk), Ardabil1 (bordering BSk), Hamadan1 (Dsa bordering BSk), Saqqez1 (Dsa), Sardasht1 (Dsa), Tabriz1 (Dsa bordering BSk), Urmia1 (bordering BSk)
- Japan: Aomori1, Asahikawa, Hakodate1, Kushiro, Mount Aso1, Mutsu1, Nagano1 (bordering Cfa), Nichinan1 (bordering Cfa), Sapporo, Tendō1 [1]
- Kazakhstan: Aktobe, Almaty, Astana, Karaganda, Oskemen, Pavlodar, Semey, Shymkent1 (Dsa), Taraz (Dsa bordering BSk)
- Kyrgyzstan: Bishkek1 (Dsa), Jalal-Abad1 (Dsa), Osh1 (Dsa)
- Mongolia: Baruunturuun (bordering Dwc), Darkhan, Kharkhorin
- North Korea: Chongjin, Haeju1, Kaesong, Kimchaek, Nampo, Pyongyang, Rason
- Russia: Abakan (bordering BSk), Barnaul, Birobidzhan, Blagoveshchensk, Chelyabinsk, Chita (bordering Dwc), Irkutsk, Khabarovsk, Krasnoyarsk, Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Kurilsk (bordering Dfc), Nakhodka, Novosibirsk, Omsk, Tomsk, Tyumen, Vladivostok, Yekaterinburg, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
- South Korea: Cheonan1, Cheongju1, Chuncheon, Chupungnyeong1, Daejeon1, Incheon1, Pyeongchang, Seoul1, Wonju, Yeongcheon1 (bordering Cfa)
- South Ossetia: Tskhinvali1 (disputed with Georgia)
- Tajikistan: Isfara1 (Dsa), Konibodom1 (Dsa), Panjakent1 (Dsa), Roghun (Dsb)
- Turkey: Ağrı (Dsb), Ardahan, Bitlis (Dsa), Çankırı1 (bordering BSk/Cfa), Çorum1 (bordering Cfa/Cfb), Erzurum, Hakkâri (Dsa), Kars, Muş (Dsa), Sivas (Dsb), Van1 (Dsa)
- Uzbekistan: Chirchiq1 (Dsa bordering Csa) [2]



- Albania: Pogradec1
- Andorra: Canillo1, El Pas de la Casa1 (bordering Dfc)
- Austria: Baden bei Wien1 (bordering Cfb) [3], Innsbruck1, Klagenfurt1, Neukirchen bei Lambach1 [4]
- Belarus: Brest1, Gomel, Minsk, Pinsk
- Bosnia and Herzegovina: Goražde1, Istočno Sarajevo1, Livno1
- Bulgaria: Pazardzhik1 (bordering Cfa), Pernik1, Pleven1, Ruse1 (bordering Cfa), Smolyan1 (Dsb), Sofia1 (bordering Cfb), Veliko Tarnovo1, Vratsa1
- Croatia: Gospić1
- Czech Republic: Brno1, České Budějovice1, Liberec1, Olomouc1 [5], Ostrava1, Plzeň1
- Estonia: Hiiumaa1, Pärnu, Saaremaa1, Tallinn, Tartu
- Finland: Åland1, Hämeenlinna, Helsinki, Kouvola, Lappeenranta, Pori, Tampere (bordering Dfc), Turku
- France: Chamonix1, Mouthe1, Saint-Véran1 (bordering Dfc)
- Germany: Ansbach1, Augsburg1 (bordering Cfb), Bayreuth1, Garmisch-Partenkirchen1, Görlitz1 (bordering Cfb), Ingolstadt1 [6], Kempten1, Sigmaringen1, Weiden in der Oberpfalz1
- Greece: Aetomilitsa1, Kato Vermio1, Samarina1, Metsovo ,Thessaloniki , Ioannina Velestino , Thasos
- Italy: Bruneck, Cortina d'Ampezzo, Rhêmes-Notre-Dame1 [7], Rocca di Mezzo1 (bordering Cfb), Toblach
- Kazakhstan: Oral (bordering BSk)
- Kosovo: Pristina1 (disputed with Serbia)
- Latvia: Daugavpils, Jelgava1, Liepāja1, Riga1
- Liechtenstein: Schaan1 (bordering Cfb)
- Lithuania: Kaunas, Klaipėda1, Šiauliai1, Vilnius
- Moldova: Bălți, Briceni, Chișinău1, Comrat1
- Montenegro: Žabljak1
- North Macedonia: Berovo1 [8]
- Norway: Bodø1 (bordering Dfc), Drammen, Hamar, Lillehammer (bordering Dfc), Oslo1, Steinkjer1, Trondheim1
- Poland: Białystok1, Bydgoszcz1, Gdańsk1, Katowice1, Kraków1, Łódź1, Lublin1, Poznań1 (bordering Cfb), Suwałki, Toruń1, Warsaw1
- Romania: Brașov, Bucharest1, Cluj-Napoca1, Iași1, Miercurea Ciuc, Ploiești1, Sibiu1, Timișoara1
- Russia: Belgorod, Bryansk, Grozny1, Kaliningrad1, Kazan, Moscow, Nalchik, Nizhny Novgorod, Orenburg, Pskov, Perm, Petrozavodsk (bordering Dfc), Rostov-on-Don, Saint Petersburg, Samara, Saratov, Smolensk, Stavropol1, Taganrog1, Tula, Ufa, Vladikavkaz1, Vladimir, Volgograd (bordering BSk), Voronezh, Yaroslavl
- Serbia: Nova Varoš1, Subotica1, Zaječar1
- Slovakia: Banská Bystrica, Košice1, Pezinok1 [9], Prešov1, Žilina1
- Slovenia: Lendava1 (bordering Cfb), Murska Sobota1
- Spain: Puerto de Navacerrada1 (Dsb bordering Csb)
- Sweden: Falun, Härnösand, Jönköping1, Kalmar1 (bordering Cfb), Norrköping1, Stockholm1, Sundsvall, Uppsala1, Visby1 (bordering Cfb)
- Switzerland: Gstaad, La Brévine (bordering Dfc), La Chaux-de-Fonds1, Poschiavo1
- Transnistria: Tiraspol1 (disputed with Moldova)
- Ukraine: Dnipro, Donetsk (occupied by Russia), Izmail1 (bordering Cfa), Kharkiv, Kherson1, Kryvyi Rih, Kyiv, Luhansk (occupied by Russia), Lviv1, Mariupol1 (occupied by Russia), Odesa1 (bordering BSk/Cfa), Uzhhorod1, Zaporizhzhia, Zhytomyr
- Brandon, MB
- Calgary (higher areas are Dwc)
- Castlegar, BC1 (Dsb bordering Dfb)
- Charlottetown
- Edmonton
- Fredericton
- Gander, NL
- Goose Bay, NL (bordering Dfc)
- Halifax
- Hamilton, ON
- Kelowna, BC1
- London, ON
- Marystown, NL1
- Moncton
- Montreal
- Moose Factory
- Murdochville, QC
- Ottawa
- Penticton, BC1 (bordering BSk)
- Prince George, BC
- Quebec City
- Red Deer, AL
- Regina (bordering BSk)
- Rimouski, QC
- Sable Island1 (bordering Cfb)
- Saint John, NB
- Saguenay, QC
- Sherbrooke, QC
- St. John's, NL
- Saskatoon (bordering BSk)
- Stewart, BC1
- Sudbury
- Sydney, NS
- Thunder Bay
- Toronto
- Trois-Rivières, QC
- Windsor
- Winnipeg
- Yarmouth, NS1
-
North Saskatchewan River valley in Edmonton
-
The Forks, with St. Boniface Cathedral in the background in Winnipeg
-
Toronto skyline taken from Colonel Samuel Smith Park in Etobicoke
-
Downtown Calgary from Southern Alberta Institute of Technology (SAIT) campus
-
Olympic Stadium in Montreal
-
Quebec City shore


- Akron, OH1
- Bismarck, ND
- Bloomington, IN1
- Cahokia Heights, IL1 (bordering Cfa)
- Cedar Rapids, IA
- Champaign, IL
- Chicago
- Cincinnati1 (downtown is Cfa)
- Cleveland1
- Columbia, MO1
- Columbus, OH1
- Dayton1
- Des Moines
- Detroit
- Duluth, MN
- Fargo, ND
- Fort Wayne, IN
- Grand Rapids, MI
- Green Bay, WI
- Indianapolis1
- Kansas City1 (bordering Cfa)
- Lansing, MI
- Lincoln, NE
- Madison, WI
- Manhattan, KS1
- Marquette, MI
- Milwaukee
- Minneapolis
- North Platte, NE
- Omaha
- Rapid City, SD (bordering BSk)
- Rochester, MN
- Rockford, IL
- Sioux Falls, SD
- South Bend, IN
- Springfield, IL1
- St. Cloud, MN
- Toledo, OH1
- Topeka1
- Youngstown, OH1



- Albany
- Allentown, PA1
- Augusta, ME
- Bangor, ME
- Binghamton, NY
- Boston1
- Bridgeport, CT1 (bordering Cfa)
- Buffalo
- Burlington, VT
- Cape Cod1 (east side is Cfb)
- Concord, NH
- Erie, PA1
- Harrisburg1 (downtown and riverfront (including City Island) are Cfa)
- Hartford1
- Lancaster, PA1 (bordering Cfa)
- Lansdale, PA1 (bordering Cfa) [10]
- Manchester, NH
- Matinicus Isle, ME1
- Morristown, NJ1
- New Haven1
- New London, CT1 (bordering Cfa)
- Newport, RI1 (bordering Cfa/Cfb)
- Paterson, NJ1 (bordering Cfa)
- Pittsburgh1
- Plymouth, MA1 (bordering Cfa)
- Portland, ME
- Portsmouth, NH
- Poughkeepsie, NY1
- Princeton, NJ1 (bordering Cfa)
- Providence, RI1
- Reading, PA1
- Riverhead, NY1 (north side facing Long Island Sound is Cfa)
- Rochester
- Scranton, PA1
- Somerville, NJ1 (bordering Cfa) [11]
- Southampton, NY1
- Springfield, MA [12]
- State College, PA1
- Syracuse
- Utica, NY
- West Chester, PA1 (bordering Cfa)
- White Plains, NY1
- Williamsport, PA1
- Worcester, MA
- York, PA1 (bordering Cfa)

- Beech Mountain, NC1
- Boone, NC1 (bordering Cfb)
- Buckhannon, WV1 (bordering Cfa)
- Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport1 (bordering Cfa)
- Clifton Forge, VA1 (bordering Cfa) [13]
- Cumberland, MD1
- Ebright Azimuth, DE1 (bordering Cfa)
- Elkins, WV1
- Emmitsburg, MD1 (bordering Cfa)
- Fairmont, WV1 (bordering Cfa)
- Hancock, MD1 [14]
- Kuwohi, NC/TN
- Mount Mitchell, NC
- Oakland, MD1
- Parkton, MD1 [15]
- Romney, WV1 (bordering Cfa) [16]
- Wheeling, WV1
- White Sulphur Springs, WV1
- Winchester, VA1 (bordering Cfa)




- Alturas, CA1 (Dsb bordering BSk/Csb)
- Aspen, CO
- Billings, MT1 (bordering BSk)
- Bozeman, MT
- Cambridge, ID (Dsa)
- Cheyenne, WY1 (bordering BSk)
- Coeur D'Alene, ID1 (Dsb bordering Csb)
- Fairbanks (bordering Dfc)
- Flagstaff, AZ1 (bordering BSk)
- Government Camp, OR1 (Dsb bordering Csb/Csc/Dsc)
- Idaho Falls (bordering BSk)
- Jackson, WY (bordering Dfc)
- Joseph, OR
- Juneau1 (bordering Dfc)
- Klamath Falls, OR1 (Dsb)
- Kodiak, AK1 (bordering Cfb/Cfc/Dfc)
- Logan, UT (Dsa)
- Los Alamos, NM1 (bordering BSk)
- Loveland, CO1 (bordering BSk)
- Mammoth Lakes, CA1 (Dsb)
- Missoula, MT
- Moscow, ID1 (Dsa)
- Mountain City, NV (bordering BSk)
- Nenana, AK (bordering Dfc)
- Ogden, UT1
- Orofino, ID1 (Dsb bordering Dsa)
- Park City, UT
- Petersburg, AK1
- Salt Lake City1 (Dsa bordering BSk/Csa)
- Santa Fe, NM1 (bordering BSk)
- Skagway, AK (Dsb bordering Dsc)
- South Lake Tahoe, CA1 (Dsb bordering Csb)
- Spokane, WA1 (Dsb bordering Csa/Csb/Dsa)
- Tahoe City, CA1 (Dsb)
- Taos, NM (bordering BSk)
- Telluride, CO
- Tusayan, AZ1 (bordering BSk)
- Winthrop, WA (Dsb)

- Falls Creek1, Victoria (bordering Dfc)
- Kiandra1, New South Wales (bordering Cfb)
- Mount Buller1, Victoria (bordering Cfb/Cfc/Dfc)
- Perisher Valley1, New South Wales (bordering Cfb/Cfc/Dfc)

- Alto Río Senguer1, Chubut Province (Dsb bordering BSk/Csb/Csc/Dsc)
- Puente del Inca1, Mendoza Province (Dsb bordering Csb)
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Continental Climate". Encyclopedia of the Atmospheric Environment. Manchester Metropolitan University. Archived from the original on 2009-04-27.
- ^ Senker, Cath (3 May 2018). Temperate Climates. Raintree Publishers. p. 5. ISBN 9781474738408. Retrieved 23 June 2023.
- ^ "Weather & Climate Change: Climates around the world". Education Scotland. Archived from the original on 14 April 2016.
- ^ Peel, M. C.; Finlayson B. L. & McMahon, T. A. (2007). "Updated world map of the Köppen–Geiger climate classification" (PDF). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 11 (5): 1633–1644. Bibcode:2007HESS...11.1633P. doi:10.5194/Hess-11-1633-2007. ISSN 1027-5606.
- ^ Kottek, Markus; Grieser, Jürgen; Beck, Christoph; Rudolf, Bruno; Rubel, Franz (2006). "World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated" (PDF). Meteorologische Zeitschrift. 15 (3): 259–263. Bibcode:2006MetZe..15..259K. doi:10.1127/0941-2948/2006/0130.
- ^ "What Is a Continental Climate?". WorldAtlas. 2019-05-21. Retrieved 2022-04-04.






